Ivana Cesarino e Alcides Lopes Leão
Professores do Dpto. de Bioprocessos e Biotecnologia da Faculdade de Ciências Agronômicas de Botucatu, UNESP
OpAA74
As aplicações do carbono
O carbono é o 4º elemento mais abundante no universo e o 15º elemento mais abundante na Terra. O nome "carbono" vem da palavra latina carbo, que significa carvão. Embora o carbono estivesse presente há séculos nas formas de fuligem e carvão, foi somente em 1772 que seus usos reais foram descobertos. Quando os átomos de carbono estão ligados em várias formas, eles são referidos como alótropos de carbono, como grafite, carbono amorfo e diamante. Ele se liga a outros átomos pequenos, incluindo outros átomos de carbono, e pode desenvolver várias ligações covalentes estáveis, formando vários compostos úteis. O biocarbono ou biochar é encontrado na forma de carvão vegetal, que são fontes sustentáveis de carbono que substituem o carvão fóssil. Estudos mostraram que o carvão vegetal pode ter um desempenho ainda melhor do que o carvão fóssil em reações químicas e, ao mesmo tempo, reduzir nossa pegada de carbono. O biochar é produzido a partir da pirólise de biomassas diversas (combustão limitada de oxigênio e temperaturas de 450 ºC a até 1350 ºC).
A lista de uso do carbono é imensa: base para a tinta em impressoras a jato de tinta; fabricação de bebidas gaseificadas; extintores de incêndio, como CO2, deslocando oxigênio; gelo seco em resfriamento; freon, em refrigeração; decorativo em joalheria; fabricação de dispositivos e ferramentas resistentes ao calor e cortadores de metal. O monóxido de carbono (CO), extraído por processo metalúrgico, é utilizado para a obtenção de diversos elementos e compostos, como redutor na conversão dos óxidos metálicos naturais em metal puro, sendo usado na fabricação de produtos como álcoois, ácidos, ésteres, etc.
O carboneto de cálcio é usado como agente de soldagem para cortar metais, preparação de acetileno e outros compostos orgânicos. As fibras de carbono contêm múltiplos usos porque têm os atributos de material leve, forte e durável. Essas fibras podem ser usadas na fabricação de varas de pesca, raquetes de tênis, foguetes e aviões.
O corpo humano contém grandes quantidades de carbono, sendo um macronutriente presente em todas as partes do corpo. O CO2 desempenha um papel importante, ajudando a manter o pH do sangue. O CO2 é um importante gás de efeito estufa que mantém a Terra aquecida, retendo a energia térmica do sol em nossa atmosfera. Todavia a humanidade está sob sério risco quando não controla a emissão antropogênica do CO2.
Várias cidades e países irão desaparecer sob os oceanos; alterações climáticas levarão à extinção seletiva de várias espécies; secas em vastas áreas; inundações; e fome por todo o planeta. O Brasil será um dos países que mais sofrerão com esses efeitos do excesso de CO2 na atmosfera.
Os diferentes usos do CO2 incluem a respiração, sendo absorvido pelas plantas durante a fotossíntese, mantendo o ciclo no ecossistema. E na fabricação de combustíveis, polímeros, fertilizantes, proteínas, etc. O negro de fumo é um pigmento preto que é tradicionalmente produzido pela carbonização de materiais orgânicos, sendo usado como reforço da borracha nas indústrias de pneus; pigmento estabilizador de UV; agente condutor ou isolante em uma variedade de aplicações; fabricação de borrachas não pneumáticas; processos construtivos e metalúrgicos; e grafite.
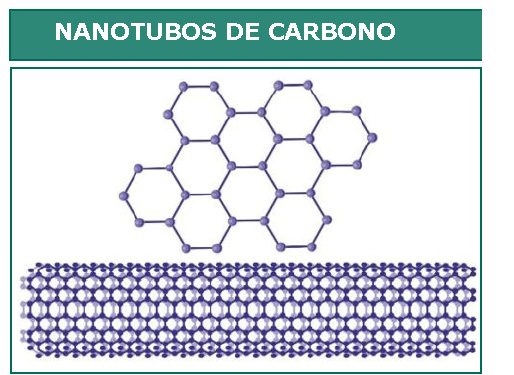
Nanotubos de carbono são moléculas cilíndricas de folhas enroladas de átomos de carbono de camada única (grafeno), conhecidas como nanotubos de carbono (CNTs). Os usos são: escovas para motores elétricos, compostas por nanotubos de carbono; ótica; emissão eletrônica de nanotubos de carbono; armazenamento de energia; condutividade elétrica em plásticos; e nanotecnologia.
Compostos de carbono ou carboidratos podem substituir os combustíveis fósseis como carvão e petróleo, sendo usados em usinas de energia, automóveis e outras indústrias (Fig. 2).
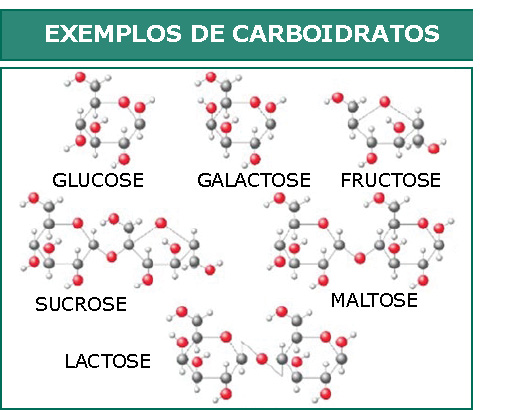
Cerca de 18% do corpo humano é composto de carbono, pois eles se comportam como blocos de construção do nosso corpo na forma de hidrocarbonetos. Peles, células, cabelos, todos são feitos de carbono. Já os carboidratos, como açúcar, glicose, frutose, maltose, etc., são os compostos de carbono que nos fornecem energia. O fenol é muito importante, usado em laboratórios e indústrias. Os ácidos carboxílicos, álcoois e compostos éstereis são usados para fazer vinagre, bebidas alcoólicas e perfumes, respectivamente.
Outro uso importante é o mercado global de plástico reforçado com carbono, que representa uma das maiores plataformas econômicas do setor, sendo dominado pelo negro de fumo produzido a partir do petróleo e, recentemente, com cargas de alta tecnologia, como fibras de carbono ou carbono nanoestruturado (nanotubos de carbono, grafeno e óxido de grafeno). Segundo dados obtidos, o grafeno de camada única é vendido a 200 €/cm2, enquanto o óxido de grafeno custa 100.000 €/kg. Por outro lado, o negro de fumo é vendido por cerca de 1 €/kg.
O carbono vegetal, ou biochar, é uma forma amorfa de carbono, produzido por pirólise, sendo um material processado por decomposição termoquímica de material orgânico a temperaturas elevadas na ausência de oxigênio, com alta área superficial e grupos funcionais abundantes.
 O componente de carbono no biochar é relativamente estável, originalmente proposto como um corretivo para armazenar carbono no solo. Biochar possui valores multifuncionais, que incluem a correção do solo; transportador de nutrientes e microbianos; agente imobilizador para remediação de metais tóxicos e contaminantes orgânicos no solo e água; catalisador para aplicações industriais; material poroso para mitigar as emissões de gases de efeito estufa e compostos odoríferos; suplemento alimentar para melhorar a saúde animal e eficiência na ingestão de nutrientes e uso em sensores eletroquímicos ou biossensores substituindo o grafeno.
O componente de carbono no biochar é relativamente estável, originalmente proposto como um corretivo para armazenar carbono no solo. Biochar possui valores multifuncionais, que incluem a correção do solo; transportador de nutrientes e microbianos; agente imobilizador para remediação de metais tóxicos e contaminantes orgânicos no solo e água; catalisador para aplicações industriais; material poroso para mitigar as emissões de gases de efeito estufa e compostos odoríferos; suplemento alimentar para melhorar a saúde animal e eficiência na ingestão de nutrientes e uso em sensores eletroquímicos ou biossensores substituindo o grafeno.
O material que passou pelo processo de pirólise mostrou um aumento da área superficial específica, o que promove melhor compatibilidade entre os componentes do compósito. Apenas como exemplo, a eliminação do negro de fumo em pigmentos graças ao uso do biochar, com 2 a 20%, e com melhoria nas propriedades mecânicas.
 O componente de carbono no biochar é relativamente estável, originalmente proposto como um corretivo para armazenar carbono no solo. Biochar possui valores multifuncionais, que incluem a correção do solo; transportador de nutrientes e microbianos; agente imobilizador para remediação de metais tóxicos e contaminantes orgânicos no solo e água; catalisador para aplicações industriais; material poroso para mitigar as emissões de gases de efeito estufa e compostos odoríferos; suplemento alimentar para melhorar a saúde animal e eficiência na ingestão de nutrientes e uso em sensores eletroquímicos ou biossensores substituindo o grafeno.
O componente de carbono no biochar é relativamente estável, originalmente proposto como um corretivo para armazenar carbono no solo. Biochar possui valores multifuncionais, que incluem a correção do solo; transportador de nutrientes e microbianos; agente imobilizador para remediação de metais tóxicos e contaminantes orgânicos no solo e água; catalisador para aplicações industriais; material poroso para mitigar as emissões de gases de efeito estufa e compostos odoríferos; suplemento alimentar para melhorar a saúde animal e eficiência na ingestão de nutrientes e uso em sensores eletroquímicos ou biossensores substituindo o grafeno.O material que passou pelo processo de pirólise mostrou um aumento da área superficial específica, o que promove melhor compatibilidade entre os componentes do compósito. Apenas como exemplo, a eliminação do negro de fumo em pigmentos graças ao uso do biochar, com 2 a 20%, e com melhoria nas propriedades mecânicas.
Biochar é um excelente aditivo para compósitos à base de fibras naturais em matrizes termoplásticas, melhorando significativamente suas propriedades, como maior estabilidade térmica, resistência à deterioração, etc. Seu peso leve o torna atraente em relação às cargas minerais, considerando, por exemplo, a redução de peso em automóveis. É produzido a partir de qualquer lignocelulósico, o que torna todo o processo mais econômico.
O carbono forma um grande número de elementos consigo mesmo (catenação), bem como com outros elementos, mostrando o quanto esse elemento é importante. Porém o carbono antropogênico, caso não seja reduzido ou utilizado em processos químicos (carboquímica), levará à total destruição do planeta.




