João Adalberto Palucci
Gerente Técnico de Tratos Culturais da RAA - Rio Amambai Agroenergia
OpAA76
Utilização de bioinsumos
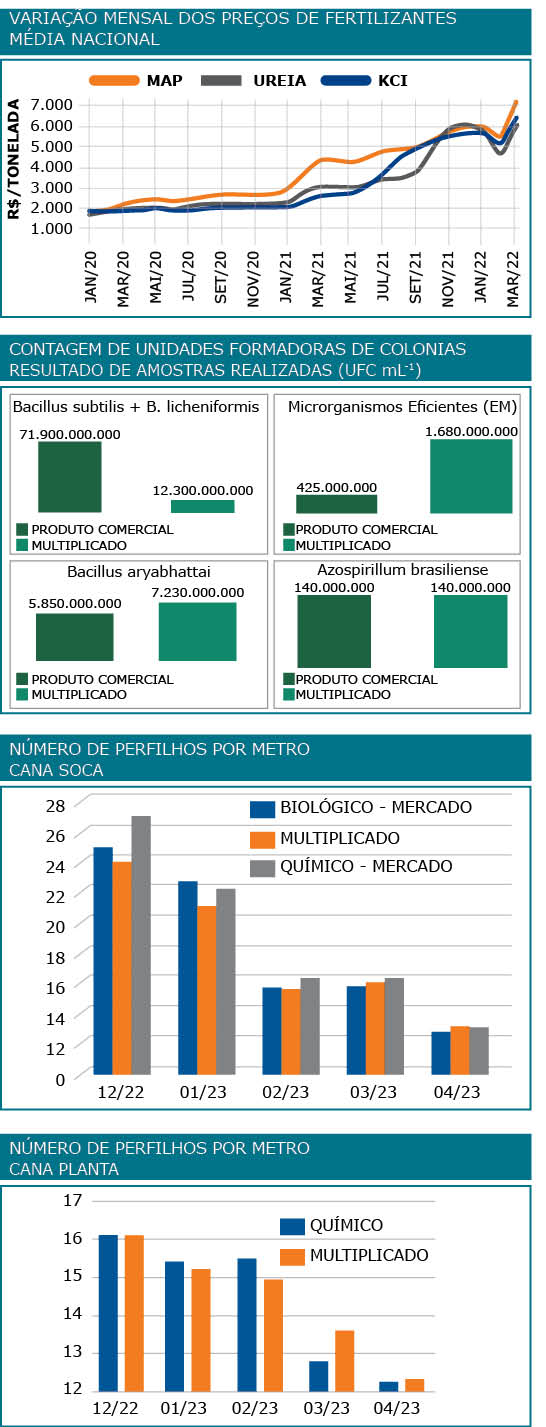 Entre 2018 e 2022, tem crescido o interesse por insumo biológicos na produção agrícola, motivado não somente pela eficiência dos produtos, como também pelo aumento do preço de fertilizantes, combustíveis e outros fatores.
Entre 2018 e 2022, tem crescido o interesse por insumo biológicos na produção agrícola, motivado não somente pela eficiência dos produtos, como também pelo aumento do preço de fertilizantes, combustíveis e outros fatores.Esse movimento vem ao encontro de uma tendência, já em curso, de utilização de matérias-primas e insumos biológicos (não sintéticos) com origem mais amigável ao meio ambiente e à saúde animal e humana dentro de uma concepção de agricultura mais sustentável; isso não se circunscreve aos fertilizantes, englobando principalmente a proteção de cultivos (como o controle biológico), a nutrição e a saúde animal, entre outras classes de produtos.
Em termos econômicos, essas práticas levam à redução da dependência de insumos importados, desvinculando, parcialmente, os custos dos produtores da variação do dólar e do custo de transporte internacional.
Temos como procedimento operacional as técnicas de produção OnFarm – do inglês, dentro da fazenda –, que trazem inúmeros benefícios ao produtor rural em função da qualidade do produto final, com menor toxicidade e maior eficiência. Empresas especializadas na produção de fábricas OnFarm montam uma estrutura que serve como base para as biofábricas, que são compostas por tanques automatizados que garantem a segurança e a qualidade do processo de produção dos bioinsumos.
Os microrganismos se multiplicam por meio de kits entregues ao produtor, como meio de cultura e sistemas anti-espuma. É preciso atenção aos detalhes e cuidados apresentados pela empresa responsável pela instalação da fábrica (principalmente na esterilização) a fim de evitar contaminações que possam inibir o processo de multiplicação das bactérias ou fungos.
Os microrganismos se multiplicam por meio de kits entregues ao produtor, como meio de cultura e sistemas anti-espuma. É preciso atenção aos detalhes e cuidados apresentados pela empresa responsável pela instalação da fábrica (principalmente na esterilização) a fim de evitar contaminações que possam inibir o processo de multiplicação das bactérias ou fungos.
Um dos grandes desafios dos produtores de cana-de-açúcar é combater pragas que atacam a lavoura. No Brasil, o clima tropical deixa esse trabalho ainda mais tenso. Tendência mundial no combate às pragas da cana-de-açúcar, o controle biológico utiliza uma série de insetos, fungos e bactérias – ou a mistura deles – para combater predadores na lavoura.
O Brasil se tornou referência mundial no controle biológico de pragas aéreas e a tática mostra-se bastante eficaz. Hoje na RAA - Rio Amambai Agroenergia dispomos de uma Biofabrica com um potencial de produção de 16.000 litros diários de multiplicado, utilizados no manejo das áreas de plantio (através do uso de estimulantes e nematicidas) e tratos de cana soca (com foco no controle de nematoides e doenças) em parte da área de cana-de-açúcar com uso de “indutores de resistência”.
O Brasil se tornou referência mundial no controle biológico de pragas aéreas e a tática mostra-se bastante eficaz. Hoje na RAA - Rio Amambai Agroenergia dispomos de uma Biofabrica com um potencial de produção de 16.000 litros diários de multiplicado, utilizados no manejo das áreas de plantio (através do uso de estimulantes e nematicidas) e tratos de cana soca (com foco no controle de nematoides e doenças) em parte da área de cana-de-açúcar com uso de “indutores de resistência”.
Nossas instalações também possuem quatro tanques de microgeo, com capacidade de 110.000 litros cada. Nessa espécie de biofábrica, primeiramente adicionamos matéria orgânica que contém microrganismos da fauna local.
Para possibilitar a sobrevivência e continuidade desses organismos, é adicionado, periodicamente, o microgeo; componente balanceado que nutre, regula e mantém a produção contínua do adubo biológico produzido, através do processo de compostagem líquida de forma contínua. Tem sido crescente a utilização dessa tecnologia. Em 2022 foram aplicados cerca de 10.000 litros numa área total de 21.000 hectares, entre plantio e soqueiras.
Para possibilitar a sobrevivência e continuidade desses organismos, é adicionado, periodicamente, o microgeo; componente balanceado que nutre, regula e mantém a produção contínua do adubo biológico produzido, através do processo de compostagem líquida de forma contínua. Tem sido crescente a utilização dessa tecnologia. Em 2022 foram aplicados cerca de 10.000 litros numa área total de 21.000 hectares, entre plantio e soqueiras.
Em 2023 serão aplicados aproximadamente 16.000 litros em um total de 22.000 hectares de áreas sob gerenciamento da unidade. Sendo assim, cerca de 15% da área total dessa propriedade recebe algum tipo de bioinsumo.
Temos focado na disponibilização de nutrientes através de microrganismos solubilizadores, que auxiliam a planta a passar por um estresse hídrico, por exemplo, de forma a não perder produtividade e, naturalmente, ajudar no controle de pragas e doenças por meio do controle direto e/ou indireto (indução de resistência).
 Utilizamos como produtos básicos:
Utilizamos como produtos básicos:
• Nematicida: bacillus subtilis + Bacillus lincheniformis;
• Enraizador: azospirillum brasiliense;
• Promotor de resistência a seca: bacillus aryabhattai;
• Condicionador de solo: microrganismos eficientes (EM);
O controle de qualidade da nossa produção é padronizado. Em momentos pré-estabelecidos, retiramos amostras para avaliação de qualidade, visando tanto a “matéria prima” como o material multiplicado.
Vale ressaltar que, quando nos referimos aos multiplicados de qualquer biofábrica, aumentamos a dose levada a campo no momento da aplicação e, atualmente, estamos utilizando cerca de 20 a 30 vezes a mais do recomendado do produto comercial puro; ainda contamos com um mix de organismos (na mesma calda/aplicação) que se sobrepõe em relação aos benefícios à planta.
Têm sido montados campos de acompanhamento dentro da unidade de operações que têm sido realizadas.
Nesse caso refere-se a uma soca de 4º corte da variedade CTC9001, ambiente de produção.
Tendo sido colhida em julho/2022, fizemos o corte da soqueira em agosto/2022 e utilizamos alguns produtos de mercado ao lado do nossos multiplicados.
No momento, o perfilhamento tem sido analisado, para a seguir ser realizada uma biometria pré-colheita prevista para agosto/2023.
É importante destacar que iniciamos as coletas dos dados em dezembro/2022.
Como observado na última avaliação, praticamente não houve diferença entre os tratamentos relacionados ao número de perfilhos; houve uma média de 5 repetições dentro de cada tratamento.
Em outra área de cana-de-açúcar, foi feito um estudo da comparação no plantio, variedade RB98 8082, ambiente de produção D, plantio em julho/2022, em que as avaliações iniciadas em dezembro/2022 serão finalizadas na colheita prevista para julho/2023.
Nesse caso refere-se a uma soca de 4º corte da variedade CTC9001, ambiente de produção.
Tendo sido colhida em julho/2022, fizemos o corte da soqueira em agosto/2022 e utilizamos alguns produtos de mercado ao lado do nossos multiplicados.
No momento, o perfilhamento tem sido analisado, para a seguir ser realizada uma biometria pré-colheita prevista para agosto/2023.
É importante destacar que iniciamos as coletas dos dados em dezembro/2022.
Como observado na última avaliação, praticamente não houve diferença entre os tratamentos relacionados ao número de perfilhos; houve uma média de 5 repetições dentro de cada tratamento.
Em outra área de cana-de-açúcar, foi feito um estudo da comparação no plantio, variedade RB98 8082, ambiente de produção D, plantio em julho/2022, em que as avaliações iniciadas em dezembro/2022 serão finalizadas na colheita prevista para julho/2023.
Os produtos utilizados no tratamento químico são padrões de mercado fungicida, nematicida e inseticida; no tratamento convencional, foi utilizado nosso multiplicado com nematicida biológico e microrganismos eficientes, o qual auxilia no sistema antiestresse hídrico da planta, e um fixador de nitrogênio; nesse último foram mantidos os inseticidas e fungicidas químicos.
Assim como no caso do tratamento da soqueira da cana, aqui também observamos que aos 270 dias que não temos diferença de perfilhamento nas condições avaliadas, ambos os experimentos têm a mesma metodologia.
Todos os locais de contagem dos perfilhos serão mantidos fixos até o final das avaliações, quando serão realizadas as biometrias.
Em ambos os campos a quantidade de perfilhos observados estão dentro do esperado pelo comportamento das variedades avaliadas.
Em ambos os campos a quantidade de perfilhos observados estão dentro do esperado pelo comportamento das variedades avaliadas.
Vale salientar que quando confrontamos os custos dos tratamentos (padrão mercado x multiplicados), observamos que o material multiplicado fica cerca de 70% mais barato que o padrão médio de mercado.




